If you are an east coast surfer, you have undoubtably experienced times when the water in the summer feels like bath water.
This is most likely due to the Gulf Stream bending in close to the coast which brings in that warm-water current.
Here is quick lesson what the Gulf Stream is, where it is, how the Gulf Stream affects climate and more.
What is the Gulf Stream?
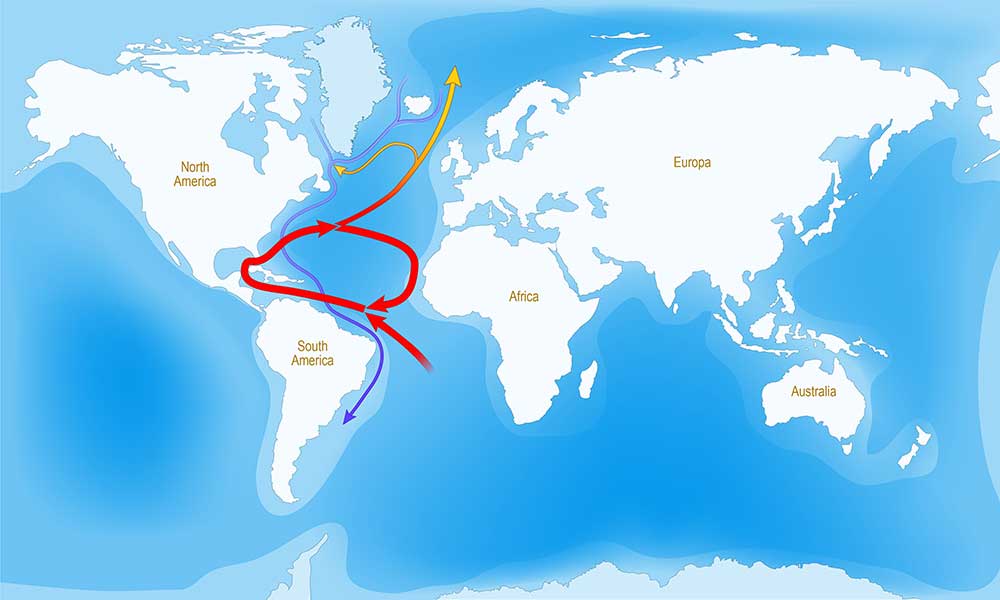
The Gulf Stream is a strong current in the Atlantic Ocean that moves warm water into the Atlantic Ocean from the Gulf of Mexico.
It extends up to Canada and the east coast of the U.S. and moves up to eastern Europe.
This occurs because the earth is always in motion, which causes multiple currents to be present in the ocean.
Scientists study the Gulf Stream via satellites to track its movement throughout the year and where it originates.
Where is the Gulf Stream?
The Gulf Stream is located in the North Atlantic Ocean and has a pattern of moving north near Florida’s coast.
It moves north before changing directions eastward close to North Carolina.
The Gulf Stream then starts to flow northeast across the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe.
How does the Gulf Stream affect the climate?
The Gulf Stream affects the climate of Florida experience a warmer climate year-round, except for in the summer when it allows the climate to feel cooler.
The Gulf Stream also causes the climate in Europe to become warmer in the western countries since it extends towards the continent.
The Gulf Stream has a significant impact on the climate in the entire Northern Hemisphere.
It’s extremely important to the global climate because it moderates the temperatures in many coastal regions of Western Europe, North America, and northwestern Africa.
What would happen if the Gulf Stream current stopped?
If the Gulf Stream suddenly stopped flowing, it would result in the ocean absorbing more sunlight and for sea ice to be eradicated.
A lot more ice would start to melt, and there would be a lower salt content in the ocean.
The result would be an increase of colder climate, particularly bringing extreme cold to Europe and portions of North America.
Sea levels would rise wreaking havoc with coastal cities as they experience more and more flooding.
You can read more about the effects if the Gulf Stream were to collapse on USA Today and on the Washington Post.
Where does the Gulf Stream flow?
The Gulf Stream flows in the western North Atlantic Ocean close to the Florida coast near the southern tip of the state.
It moves north all the way to the coast of Ireland after passing the eastern boundary of the U.S.
Powerful winds and a few large currents drive the movement of the gulf coast, causing colder water to sink as warm water moves into the stream.
The Gulf Stream moves the fastest closest to the surface of the water and travels at an average speed of four miles per hour.
It has a maximum speed of 5.6 miles per hour.
New studies suggest the gulf is currently moving at a slower speed in recent years.
This can eventually result in a change in weather and can lead to more severe storms and hurricanes.
There’s a chance of the winter storm track coming off the Atlantic.
If the Gulf Stream became weaker, it would also cause the sea levels to rise on the Atlantic coast, which could be disastrous.
How wide is the Gulf Stream?
The Gulf Stream measures approximately 40 to 50 miles wide off the southwest Florida coast.
It snakes and chugs towards Iceland at two to four miles per hour. Scientists have found it to measure 3,900 feet deep.
It starts to circulate in the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico, where it’s most visible by satellites.
This shows that the Gulf of Mexico is where it begins.
Do hurricanes follow the Gulf Stream?
Hurricanes tend to follow the Gulf Stream and start to intensify because the warm water is used as energy for the hurricane, causing them to become a lot stronger and powerful.
The more the temperatures rise in the water, the more energy the hurricanes get from the Gulf Stream.
The Loop Current can also affect hurricanes and their strength before they touch down and have contact with land.
The currents cause the hurricanes to follow similar paths over time.
Want to know more about hurricanes? Check out When Is Hurricane Season.
What are the Loop Current and the Gulf Stream?
The Loop Current travels from the Caribbean while passing the Yucatan Peninsula before reaching the Gulf of Mexico.
It consists of warm water and flows directly into the Florida Strait before moving past it.
Once it reaches the Gulf of Mexico, it moves north towards the east coast of the United States.
The temperature of the water in the Loop Current is 80 degrees Fahrenheit.
As a strong ocean current, the Gulf Stream transports warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to the Atlantic Ocean.
There are safe places that people can swim in the Gulf Stream near the Gulf beaches.
Most people spend time in this area because of how comfortable the warm water is to swim in throughout the year.
The water in the Gulf Stream is up to 71 degrees Fahrenheit.
It’s considered to be an intense, warm current.